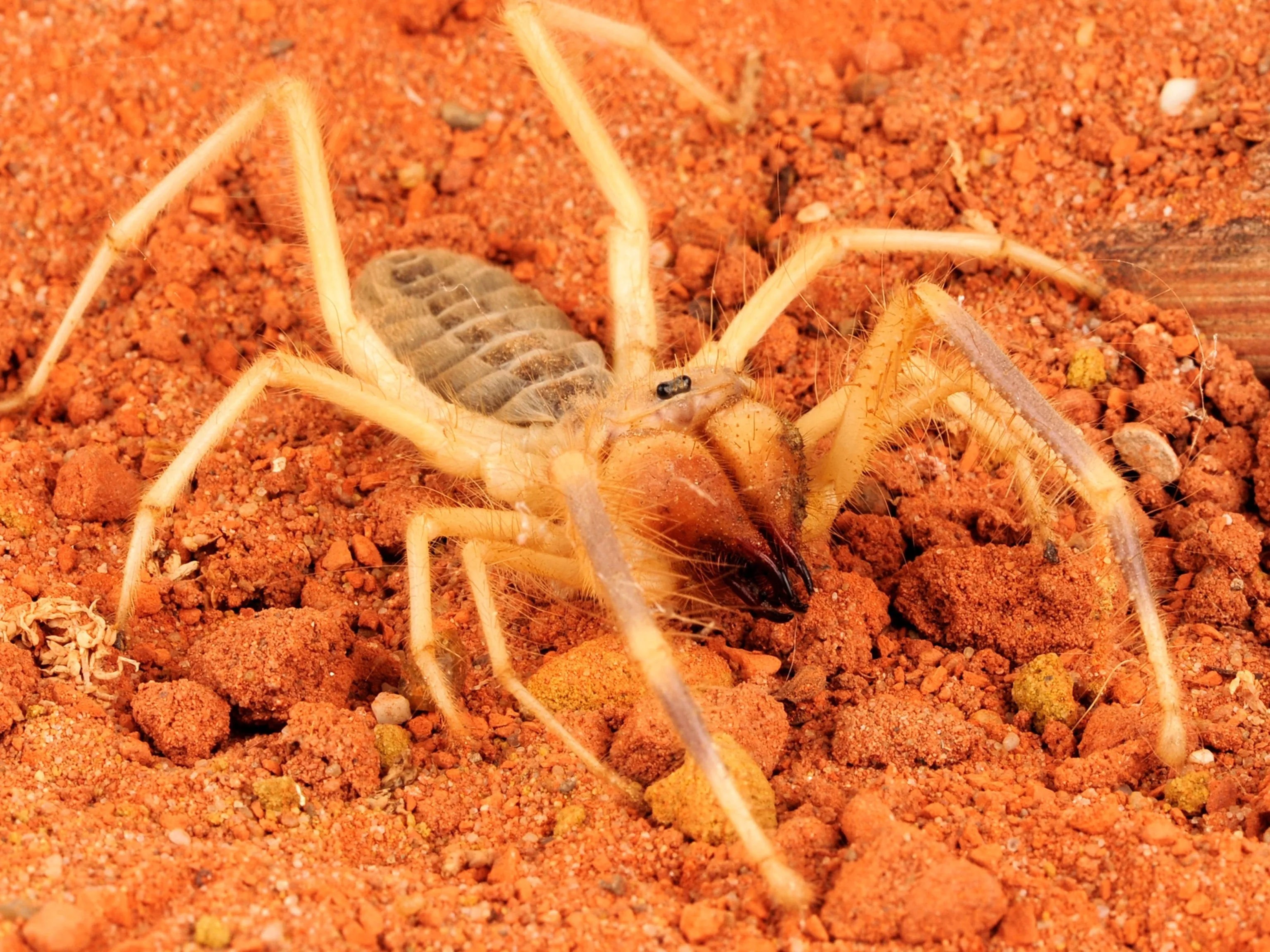
Camel Spider vs Tarantula Size: Fact 1
The size difference between a camel spider and a tarantula is a common point of fascination, often sparking debates about which is larger or more formidable. While both are arachnids, their sizes can vary significantly depending on the species and individual circumstances. Camel spiders, also known as wind scorpions or solifuges, are often perceived as being larger due to their elongated bodies and impressive jaws. However, tarantulas, being true spiders, generally have a larger body mass and leg span. The perception of size can be misleading without considering the specific measurements and characteristics of each arachnid.
Camel Spider Size
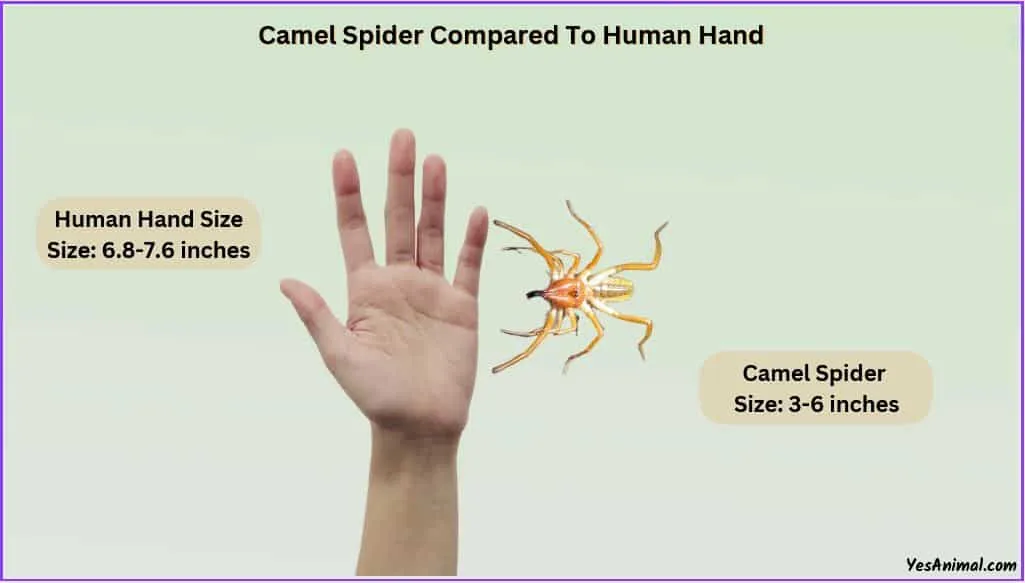
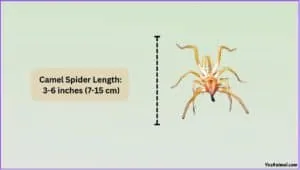
Camel spiders are known for their relatively large size, especially in proportion to their body. They typically range from 4 to 6 inches (10 to 15 cm) in length, including their legs. The body itself is usually around 1 to 3 inches long, with powerful jaws that can be nearly as long as their heads. These jaws, or chelicerae, are used for grabbing and crushing prey, contributing to their intimidating appearance. Their legs are also quite long, which helps them move quickly across the ground. The overall size can vary depending on the species and the availability of food and resources in their environment.
Factors Influencing Camel Spider Size
Several factors influence the size of camel spiders. The most important is the availability of food. A diet rich in insects, small lizards, and other invertebrates can promote larger growth. Environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, also play a role, with warmer climates often supporting larger sizes. Genetic factors, including the specific species, also contribute to the ultimate size a camel spider reaches. Some species are naturally larger than others, demonstrating a range of sizes within the solifuge family. Understanding these factors helps to appreciate the variability in camel spider size across different populations.
Tarantula Size
Tarantulas, in contrast to camel spiders, are known for their substantial body size and leg span. They can range from 3 to 12 inches (7.6 to 30 cm) in leg span, with some of the largest species reaching or exceeding this size. The body itself can be up to 4 inches (10 cm) long in some cases. Their size is an adaptation for hunting, allowing them to capture larger prey, including insects, small rodents, and birds. Tarantulas are among the largest spiders in the world, and their imposing size often makes them a focal point of attention.
Factors Influencing Tarantula Size
Tarantula size is influenced by a variety of factors similar to camel spiders. Diet is crucial; a consistent diet of insects and small animals is essential for growth and molting. Genetics also play a significant role, as certain species are naturally larger than others. Environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, also impact their development. Furthermore, the tarantula’s life cycle, including the number of molts it undergoes, affects its ultimate size. Factors such as the availability of suitable habitats also indirectly influence their size, as well-nourished tarantulas tend to grow larger.
Camel Spider vs Tarantula Size: Fact 2

Camel Spider Appearance and Characteristics
Camel spiders have a distinct appearance that makes them easily recognizable. They have a pair of large chelicerae (jaws) that protrude prominently from the front of their body, used for grasping and crushing prey. Their bodies are segmented, with a cephalothorax and abdomen. They have eight legs, the front two of which are often used as sensory organs rather than for walking. They are typically tan or brown in color, providing camouflage in their desert and arid habitats. Their fast movements and aggressive behavior also define their image.
Tarantula Appearance and Characteristics
Tarantulas are characterized by their large, hairy bodies and impressive leg spans. Their bodies are divided into two main parts the cephalothorax and the abdomen. They have eight legs that are covered in sensory hairs. They also have chelicerae but they are not as prominent as those of camel spiders, but still used for injecting venom and manipulating prey. Their bodies come in a wide variety of colors and patterns, depending on the species, and they are often covered in dense hairs. Their size and appearance make them a noticeable presence in their natural environment.
Camel Spider vs Tarantula Size: Fact 3
Habitat and Geographic Distribution of Camel Spiders
Camel spiders are primarily found in arid and semi-arid environments. They are common in deserts, grasslands, and scrublands. Their geographic distribution includes regions in the Middle East, Africa, and the southwestern United States. They are nocturnal hunters, spending their days hidden under rocks, in burrows, or under other sheltered locations. Their habitat provides them with cover from the sun and predators, as well as a source of prey. The ability to thrive in harsh environments is a key feature of their lifestyle.
Habitat and Geographic Distribution of Tarantulas
Tarantulas are found in a variety of habitats, including tropical rainforests, grasslands, and deserts. Their distribution spans across the Americas, Africa, Asia, and Australia. They can be found in burrows, under rocks, or in trees, depending on the species. Some tarantulas are terrestrial, while others are arboreal. Their habitat preferences are closely tied to their specific needs for shelter, prey availability, and suitable climate conditions. Different species have adapted to distinct environments, resulting in a wide range of habitats.
Camel Spider vs Tarantula Size: Fact 4
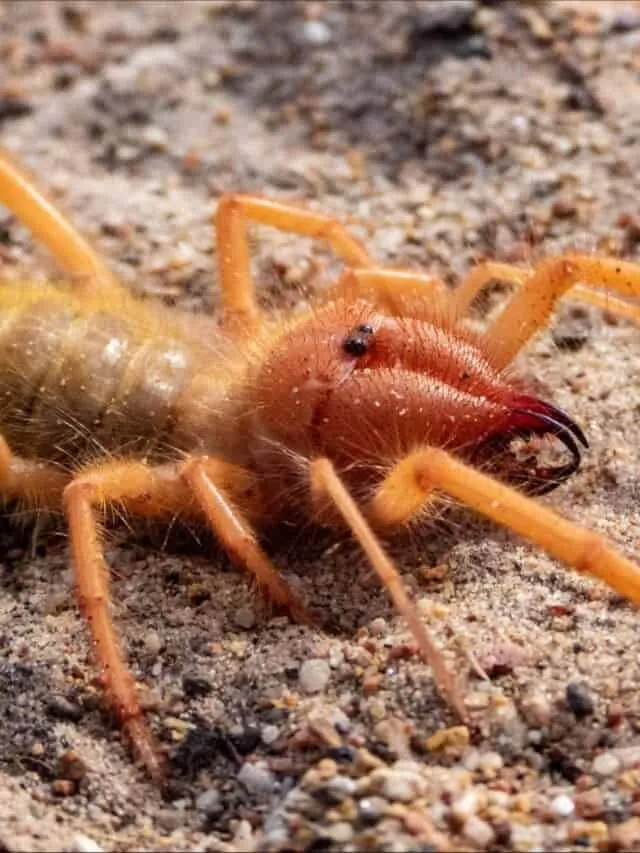

Diet and Feeding Habits of Camel Spiders
Camel spiders are voracious predators with a diet consisting primarily of insects, other arachnids, and small vertebrates. They are opportunistic hunters, often ambushing their prey. They use their powerful jaws to crush their victims and consume them. They are known for their aggressive feeding behavior, which contributes to their fearsome reputation. Their diet plays a significant role in their growth and survival, and they are adapted to hunt in the challenging conditions of their habitats.
Diet and Feeding Habits of Tarantulas
Tarantulas are also carnivorous predators, consuming insects, other arachnids, and occasionally small vertebrates like mice and birds. They use their fangs to inject venom, which immobilizes their prey. The venom also helps in breaking down the tissues for easier digestion. They typically ambush their prey or actively hunt, depending on their species. Their diet supports their large size, with consistent feeding essential for their growth and health.
Camel Spider vs Tarantula Size: Fact 5
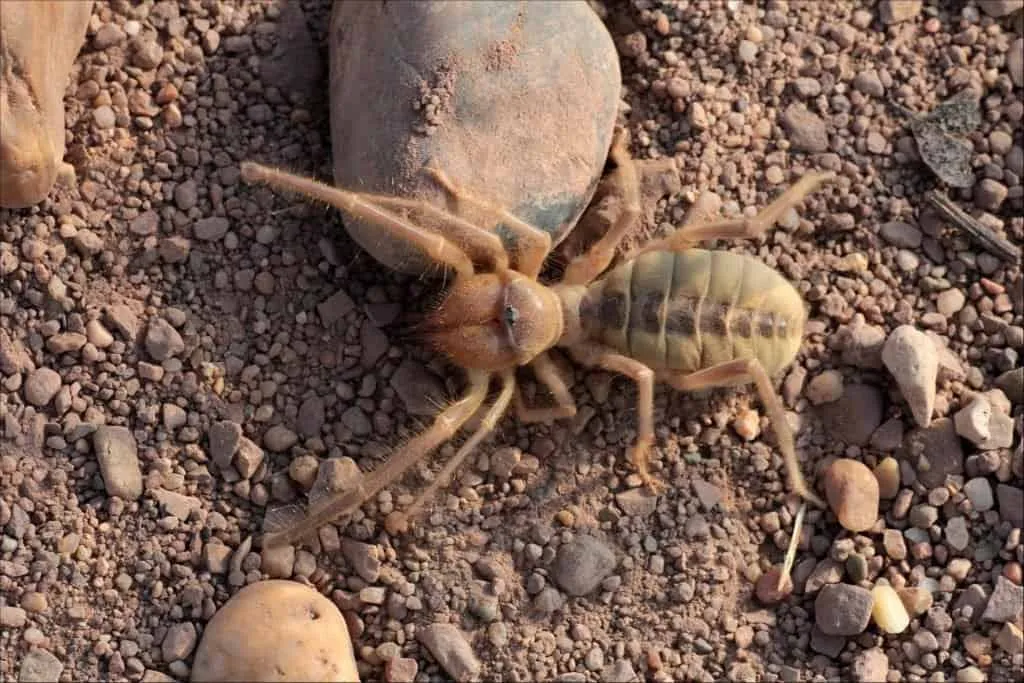

The Importance of Size in Survival and Behavior
Size plays a critical role in the survival and behavior of both camel spiders and tarantulas. Larger size often equates to a greater ability to hunt and compete for resources. In camel spiders, their size allows them to overpower prey and defend against predators. In tarantulas, their size provides an advantage in hunting and protecting themselves. Size can influence their social interactions, with larger individuals sometimes having dominance. The size of each arachnid is an adaptation to their specific environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while both camel spiders and tarantulas are fascinating arachnids, their size varies significantly and plays a crucial role in their survival and behavior. Camel spiders are often perceived as large because of their body length and jaws, while tarantulas boast impressive leg spans and overall body mass. Factors such as diet, genetics, and habitat conditions influence size. Understanding the size differences and associated characteristics of these creatures provides valuable insights into their ecological roles and adaptations.
