Understanding the Tevo Tarantula Pro
The Tevo Tarantula Pro is a popular and affordable 3D printer, perfect for beginners and experienced makers alike. Its open-frame design and ease of use make it a great entry point into the world of 3D printing. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know to get started with your Tevo Tarantula Pro, from assembly to your first successful print. The Tarantula Pro offers a decent build volume, allowing for the creation of a variety of projects, and is often praised for its value for money. Before diving into the details, let’s familiarize ourselves with the key aspects of this machine, so you can make informed decisions when working with it.
Key Features of the Tevo Tarantula Pro
The Tevo Tarantula Pro comes with several features that set it apart. It typically includes a heated bed for printing with various materials, a color touchscreen for easy navigation, and a sturdy frame to ensure stability during printing. The printer’s open-source nature means you can customize it, upgrade parts, and print with various filaments, giving you immense flexibility. Furthermore, the easy-to-assemble design contributes significantly to its appeal among hobbyists and educators. These key features, coupled with the affordability factor, make it a great choice for those looking to dive into 3D printing without breaking the bank.
Technical Specifications of the Tevo Tarantula Pro

Understanding the technical specifications is crucial. The Tevo Tarantula Pro usually offers a build volume of around 220 x 220 x 220 mm, providing ample space for most projects. It supports a variety of filament types, including PLA, ABS, PETG, and more. The printer’s nozzle diameter is typically 0.4mm, but you can upgrade to different sizes. The operating voltage is usually 12V or 24V, and the printer connects to your computer via USB or an SD card. The specifications provide a solid foundation for understanding the capabilities of the Tevo Tarantula Pro, helping you make informed choices regarding materials and print settings. Make sure to refer to the specific model’s manual for exact figures.
Assembling Your Tevo Tarantula Pro
Assembling your Tevo Tarantula Pro might seem daunting, but the process is straightforward with patience and following instructions. The printer comes as a kit, and the assembly process is an excellent way to understand the printer’s mechanics. Proper assembly ensures the printer’s stability and print quality, so taking your time is essential. This section will break down the process, making it manageable, even if you’ve never assembled a 3D printer before. Carefully unpack all the components and organize them, ensuring nothing is missing before you start the build process.
Tools and Materials Needed
Gathering the right tools and materials is the first step in assembling the Tevo Tarantula Pro. Most of the required tools are provided, but you’ll want to have a few extras handy. You’ll need a set of Allen wrenches (typically provided, but having a backup is a good idea), a small Phillips head screwdriver, a pair of wire cutters, and possibly some zip ties. Check the parts list to make sure you have all the necessary components. Good lighting and a clear workspace will make the assembly process easier. Be sure to have the manual close by as well, so you can easily refer to the instructions throughout.
Step-by-Step Assembly Guide
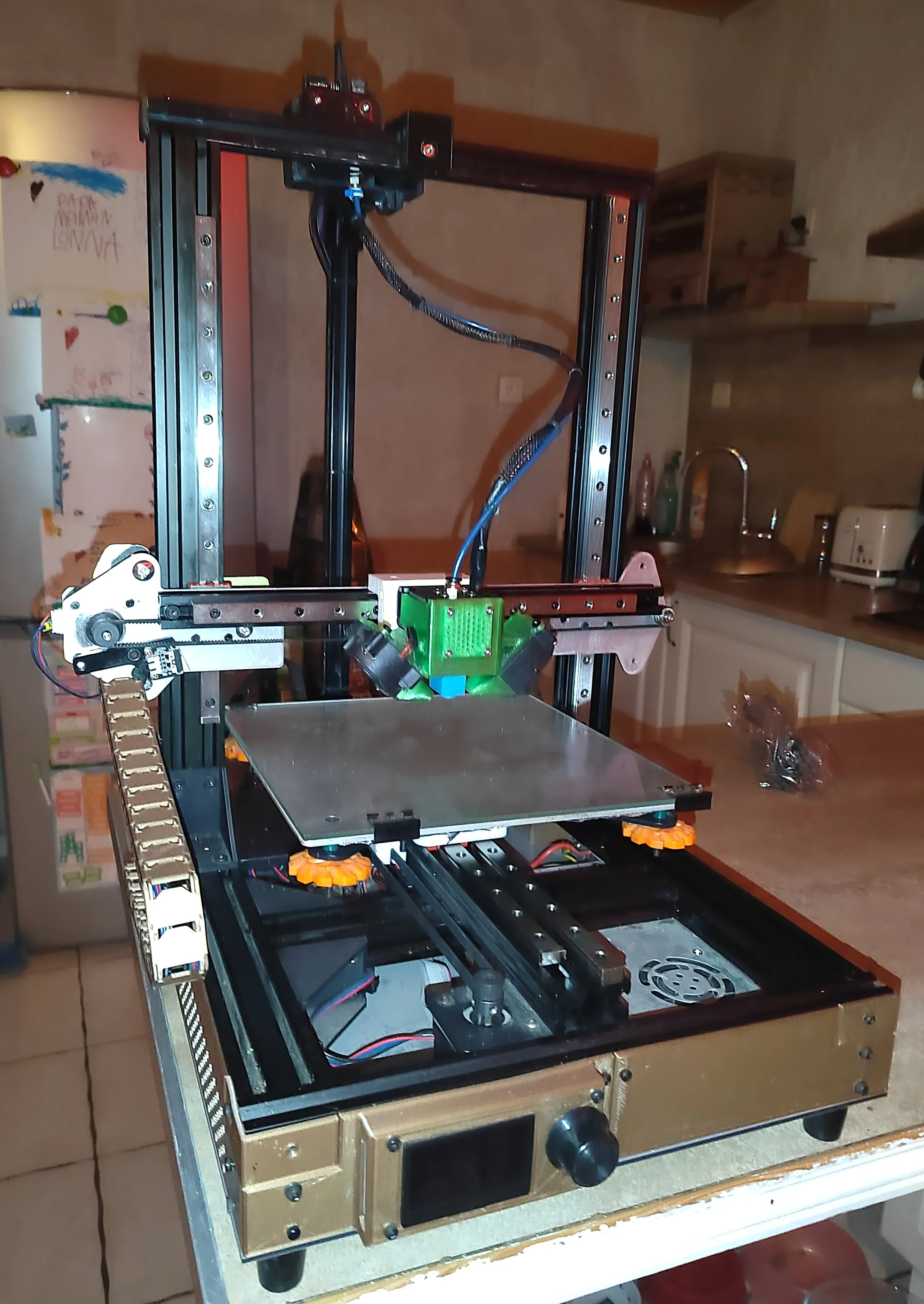
Begin by assembling the frame, usually consisting of attaching the vertical supports to the base. Use the provided screws and Allen wrench to secure the pieces, ensuring everything is square. Next, attach the heated bed and the X, Y, and Z axis components. Follow the manual’s instructions closely, making sure to tighten all screws properly. The wiring can be a bit tedious, but the manual should provide clear diagrams to help you connect the motors, endstops, and hot end components. Once assembled, double-check all connections and ensure everything moves smoothly before moving forward.
Connecting the Electronics
Wiring is a critical step. Carefully connect all the electronic components according to the manual. Pay close attention to the polarity of the wires and the correct placement of connectors. Incorrect wiring can damage your printer. Common components include the stepper motors, the heated bed, the hot end, and the display. Often, connectors are keyed to prevent incorrect insertion, but double-check everything. It’s a good idea to take a picture before disconnecting any wires, as this can help you with reassembly if needed. This can save you considerable time during the setup phase.
Leveling the Print Bed
Bed leveling is one of the most critical steps for successful 3D printing. Proper bed leveling ensures the first layer of your print adheres to the bed, preventing warping or detachment during the print. There are several methods for bed leveling, and the Tevo Tarantula Pro offers both manual and automatic options. This section explores both methods, so you can choose the one that best suits your preferences. Mastering this skill will dramatically improve your print quality and overall printing experience. The correct setup is key to any successful printing session.
Why Bed Leveling is Crucial

Bed leveling ensures the first layer of your print adheres correctly to the print bed. If the bed is too far from the nozzle, the filament won’t stick, resulting in failed prints. If the bed is too close, the nozzle can scratch the bed, and the filament will be squished, leading to other printing issues. Proper leveling creates the ideal distance between the nozzle and the bed, allowing the filament to bond and create a solid foundation for your prints. Skipping this step almost always leads to print failures. Bed leveling is essential to producing high-quality and reliable prints.
Manual Bed Leveling Instructions
Manual bed leveling involves adjusting the bed’s height at various points using the leveling screws, typically located at each corner of the bed. Heat the bed to your printing temperature. Using a piece of paper (or the provided card) between the nozzle and the bed, move the nozzle to each corner and adjust the leveling screws until the paper offers a slight resistance when you slide it. Repeat this process several times, moving from corner to corner, until the paper resistance is consistent across the entire bed. Many users find that this process requires patience, but it is crucial. You can also use the printer’s menu to move the print head to each corner for adjustment.
Auto Bed Leveling Setup
Some Tevo Tarantula Pro models come with or can be upgraded with an auto-bed leveling (ABL) sensor. This sensor automatically measures the distance between the nozzle and the bed at various points, compensating for any unevenness. To set up ABL, you’ll need to install the sensor, connect it to the printer’s control board, and configure the firmware. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to calibrate the sensor and set the Z-offset, which determines the distance between the nozzle and the bed during printing. The ABL system significantly simplifies the bed-leveling process and can improve print consistency. Once you have the sensor installed and calibrated, you should always start your print with the ABL enabled.
Slicing Your First Print

Slicing software converts 3D models into instructions your printer can understand. This process is essential for preparing your models for printing. The slicer generates G-code, which is a set of commands that control the printer’s movements, temperature, and other settings. Choosing the right slicing software and configuring the appropriate settings is key. This section will guide you through selecting slicer software and setting the basic configurations required to begin your first print. Selecting the right settings ensures a successful print.
Choosing Slicing Software
Several free and paid slicing software options are available. Popular choices include Cura, Simplify3D, PrusaSlicer, and others. Cura is an excellent option for beginners due to its user-friendly interface and extensive feature set. When choosing software, consider the learning curve, available features, and compatibility with your printer. Cura is widely used, and there are many online resources. Other software may offer advanced features, but are more complicated to use. Experimenting with different software packages will help you find the one that best suits your needs.
Configuring Basic Print Settings
Once you’ve chosen your slicing software, you’ll need to configure the basic print settings. These settings include the nozzle temperature, bed temperature, layer height, print speed, and infill density. The ideal settings depend on the filament type you’re using. PLA typically prints at around 200°C for the nozzle and 60°C for the bed, while ABS requires higher temperatures. Layer height affects the print quality and print time. Lower layer heights produce higher-quality prints but take longer. Print speed also affects print time and quality. Experimenting with these settings is essential to achieve the best results. Start with the recommended settings and adjust based on your print quality and performance.
Loading Filament and Preparing to Print

After setting up the slicer, the next step is loading filament and preparing your printer. Correct filament loading is critical to a successful print. Before starting, make sure you have the correct filament type for your project. Incorrect filament choice can lead to print failures. This section will help you load your filament properly and prepare your printer for the first print. Careful preparation minimizes the risk of problems during printing, making your experience far more enjoyable. Remember that filament quality can make a significant difference.
Filament Types and Their Properties
The most common filament types for 3D printing are PLA, ABS, PETG, and TPU. PLA (Polylactic Acid) is easy to print with and ideal for beginners. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is more durable but requires a heated bed and enclosure. PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) offers a good balance of strength and ease of printing. TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) is flexible and used for printing rubber-like parts. Each filament has unique properties, influencing the print settings and the intended use of your prints. Consider the project’s requirements when selecting your filament.
Loading Filament Properly
To load filament, first, heat up the hot end to the recommended temperature for your filament type. Insert the filament into the extruder and gently push it until it comes out of the nozzle. Make sure the filament feeds smoothly and is not tangled. You might need to manually extrude a small amount of filament to ensure the nozzle is clear and the flow is consistent. If the filament doesn’t extrude properly, check for clogs or issues with the extruder. Correct filament loading ensures the printer can execute the G-code commands from your slicer software.
Initial Print Setup and Testing

After completing the assembly, bed leveling, slicing, and filament loading, it’s time for your first print. This crucial step will confirm the success of your setup. Before launching a complex project, begin with a test print, such as a small calibration cube or a benchy. This will allow you to assess the print quality and identify any issues. This section will explore initial print setup and testing, providing instructions for the initial print and troubleshooting for any problems.
Testing the First Layer Adhesion
The first layer is the foundation of your print, so ensuring good adhesion is critical. Observe the first layer as it prints, making sure the filament adheres to the bed without curling or lifting. If the filament doesn’t stick, adjust the bed leveling and nozzle height. Too close to the bed, and the nozzle may scratch the bed. Too far, and the filament won’t stick. The first layer should be smooth, consistent, and without gaps. A good first layer lays the foundation for the entire print, so spend time to get it right. Proper adhesion ensures that the model stays in place throughout the printing process.
Troubleshooting Common Printing Issues
Even with careful setup, you might encounter printing issues. Common problems include warping, stringing, and poor layer adhesion. Warping occurs when the edges of your print lift off the bed, usually due to cooling. Stringing is caused by filament oozing from the nozzle during travel moves. Poor layer adhesion can cause the print to separate. To troubleshoot, experiment with settings, such as the bed temperature, nozzle temperature, and print speed. Check for clogs in the nozzle, make sure your bed is clean, and consider using a brim or raft for better adhesion. Remember, 3D printing takes practice. Embrace troubleshooting as part of the learning process.
Congratulations! You’ve taken the first steps to 3D printing with your Tevo Tarantula Pro. Enjoy the process of experimenting and learning. Happy Printing!
